Spring Security 是一个强大、灵活的安全框架,广泛用于保护 Java 应用程序。随着 Spring Boot 3 和 Java 17 的引入,Spring Security 继续增强其功能,为开发者提供了更简化的配置和现代化的安全实践。
本文将详细介绍如何在 Spring Boot 3 中集成 Spring Security,涵盖基本认证、密码加密等核心功能。
1. 简介与概念
Spring Security 提供了基于身份验证(Authentication)和授权(Authorization)的安全模型。身份验证是验证用户身份的过程,而授权则是决定用户是否有权访问资源。
核心组件:
- SecurityFilterChain:负责定义 HTTP 请求的安全过滤链。
- UserDetailsService:用于加载用户信息,提供身份验证。
- PasswordEncoder:处理用户密码的加密与解密。
2. 基础配置
Spring Boot 3 使用自动配置来简化 Spring Security 的集成。但在许多实际场景中,我们需要自定义安全配置,下面介绍基本的 Spring Security 配置步骤。
2.1. 添加依赖
首先,在 pom.xml 中添加 Spring Security 依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
接着,在 application.yml 中配置安全设置。
2.1 基本认证与授权配置
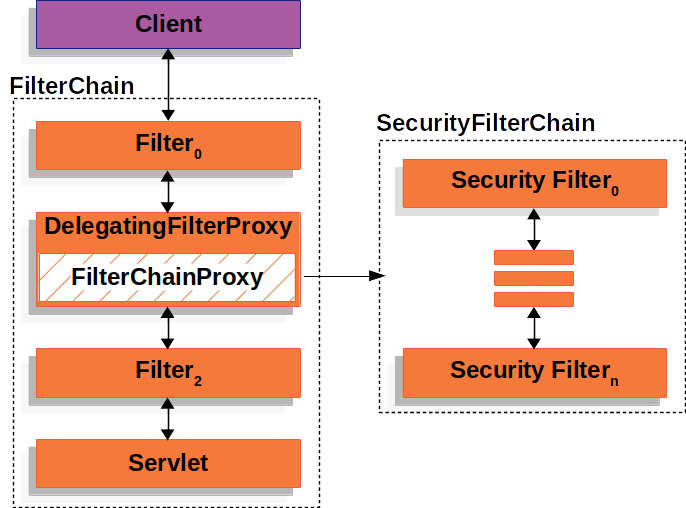
首先,我们通过创建 SecurityConfig 类来自定义 Spring Security 的配置。该配置类通常需要实现 SecurityFilterChain,Spring Security 通过过滤器链的方式来处理 HTTP 请求。过滤器链由一系列的过滤器 (Filter) 组成,这些过滤器按照配置的顺序依次处理请求。每个过滤器完成特定的安全检查或操作(如身份验证、授权、会话管理等),然后将请求传递给下一个过滤器。
示例代码:
package com.coderjia.boot313security.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.security.config.Customizer;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.provisioning.InMemoryUserDetailsManager;
import org.springframework.security.web.SecurityFilterChain;
/**
* @author CoderJia
* @create 2024/10/13 下午 01:57
* @Description
**/
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig {
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeHttpRequests(auth -> auth
.requestMatchers("/").permitAll() // 公开访问
.anyRequest().authenticated() // 其他接口需认证
)
.formLogin(Customizer.withDefaults())
.httpBasic(Customizer.withDefaults()); // 使用 HTTP Basic 认证
return http.build();
}
@Bean
public UserDetailsService userDetailsService(PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder) {
// 创建用户
UserDetails user = User.builder()
.username("coderjia")
.password(passwordEncoder.encode("cj123456"))
.roles("USER")
.build();
return new InMemoryUserDetailsManager(user);
}
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder(); // 使用 BCrypt 进行密码加密
}
}
解释:
SecurityFilterChain定义了所有 HTTP 请求的安全策略。在这里,/路径对所有人公开,而其他路径需要用户身份认证。UserDetailsService提供了用户的详细信息,包括用户名、密码及角色。在这个例子中,我们创建了一个用户名为 "user" 的用户,密码为 "password"(经过加密处理),并分配了 "USER" 角色,如果不配置,系统则会在日志中输出名为 user 的用户对应的密码:Using generated security password: b9fe7857-97a3-4db7-9602-9e10db56496d。PasswordEncoder通过BCryptPasswordEncoder实现密码加密,以确保用户密码存储时是安全的。@EnableWebSecurity注解启动 Spring Security 的自动配置,使得应用能够自动集成 Spring Security 提供的安全功能。
3. 密码加密
Spring Security 强烈建议使用加密算法对密码进行加密,防止敏感信息泄露。在 Spring Boot 3 中,BCryptPasswordEncoder 是一种常用的加密方式。它基于 bcrypt 算法,提供了足够的强度和安全性。
3.1. 如何加密用户密码
- 在
UserDetailsService中,我们通过passwordEncoder.encode("password")对用户密码进行加密。 - 在身份验证时,Spring Security 会自动使用同样的加密算法进行密码比对。
3.2. 自定义密码加密器
如果需要自定义密码加密算法,可以实现 PasswordEncoder 接口。以下是自定义加密器的简单示例:
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder(10); // 设置加密强度
}
在这个示例中,我们为 BCryptPasswordEncoder 提供了加密强度参数,值越大,安全性越高,但加密速度会相对减慢。BCryptPasswordEncoder 的默认实现使用 BCryptPasswordEncoder 的 Javadoc 中提到的强度10。
// Create an encoder with strength 16
BCryptPasswordEncoder encoder = new BCryptPasswordEncoder(16);
String result = encoder.encode("myPassword");
System.out.println(encoder.matches("password", result));
或者使用 SpringBoot CLI 对密码进行加密:
$ spring encodepassword password

4. 表单登录与自定义登录页面
除了 Basic 认证,Spring Security 还支持表单登录。通过 formLogin() 方法,可以启用表单认证,也提供自定义的登录页面。
http
.formLogin(Customizer.withDefaults() // 使用默认登录
4.1. 自定义表单登录配置
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeHttpRequests(auth -> auth
.requestMatchers("/").permitAll() // 公开访问
.anyRequest().authenticated()
)
.formLogin(form -> form
.loginPage("/login") // 自定义登录页面
.permitAll() // 登录页面无需认证
)
.logout(logout -> logout.permitAll()); // 允许注销
return http.build();
}
在这里,我们自定义了登录页面 /login,并允许用户访问登录功能而无需认证,提供接口 /index 返回 index.html 页面:
@GetMapping("/login")
public String login() {
return "login"; // 返回名为 "login" 的模板或 HTML 页面
}
4.2. 定义控制器
package com.coderjia.boot313security.controller;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
/**
* @author CoderJia
* @create 2024/10/13 下午 02:10
* @Description
**/
@Slf4j
@Controller
public class LoginController {
@GetMapping("/login")
public String login() {
return "login"; // 返回名为 "login" 的模板或 HTML 页面
}
@GetMapping("/index")
public String home() {
log.info("index");
return "index"; // 返回名为 "index" 的模板或 HTML 页面
}
@ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/admin")
public String admin() {
log.info("admin");
return "欢迎进入管理页面";
}
}
4.3. 自定义登录界面
提供一个简单的首页页面和登录页,这里使用了 thymeleaf 摸板,详细请参考重学SpringBoot3-集成Thymeleaf:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title>Main Page</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Welcome to my page</span>!</h2>
<a th:href="@{/admin}">访问受限资源</a>
<br/>
<a th:href="@{/logout}">Logout</a>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:th="https://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title>Please Log In</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Please Log In</h1>
<div th:if="${param.error}">
Invalid username and password.</div>
<div th:if="${param.logout}">
You have been logged out.</div>
<form th:action="@{/login}" method="post">
<div>
<input type="text" name="username" placeholder="Username"/>
</div>
<div>
<input type="password" name="password" placeholder="Password"/>
</div>
<input type="submit" value="Log in" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
4.4. 测试登录
进入首页,此时不需要登录!
点击 访问受限资源 /admin 要求认证,进入我们自定义的登录页。
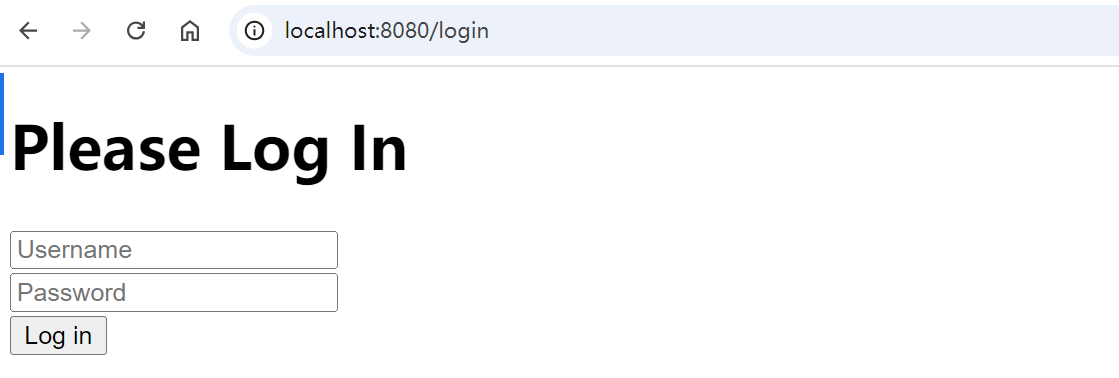
输入设置的用户名和密码之后,认证通过,进入 /admin 页面:
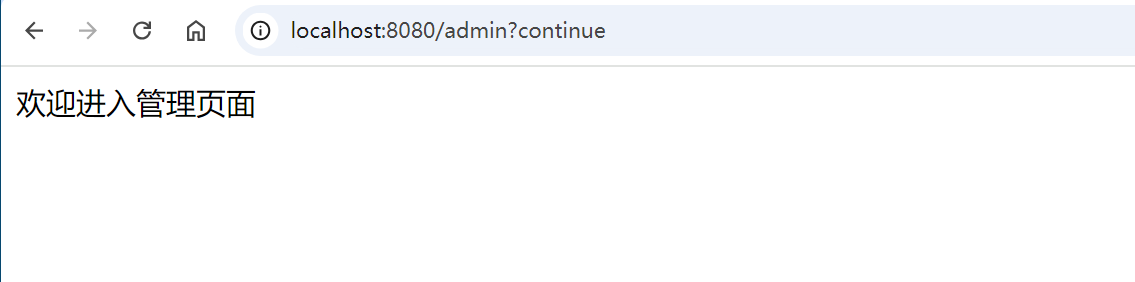
5. 注销
有登录,同样也提供了登出,默认情况下,Spring Security 会建立一个 /logout 端点,所以不需要额外的代码。当你包含 spring-boot-starter-security 依赖或使用 @EnableWebSecurity 注解时,Spring Security 将添加其注销支持,并默认响应 GET /logout 和 POST /logout。
注意,Spring Security 默认开启了防 CSRF 攻击,注销时需要提供 csrf_token,直接调用 GET /logout 会提示 404,只能能通过 POST 请求,
<form th:action="@{/logout}" method="post">
<button type="submit">Logout</button>
</form>
如果强制要使用 GET 请求,则需要修改成以下配置形式:
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.csrf(Customizer.withDefaults())
.authorizeHttpRequests(auth -> auth
.requestMatchers("/").permitAll() // 公开访问
.anyRequest().authenticated() // 其他接口需认证
)
.formLogin(form -> form
.loginPage("/login")
.permitAll()
)
.logout((logout) -> logout
.logoutRequestMatcher(new AntPathRequestMatcher("/logout"))
)
.httpBasic(Customizer.withDefaults()); // 使用 HTTP Basic 认证
return http.build();
}
6. 总结
Spring Security 包含的概念很多,本节先简单介绍了其认证功能、用户定义和密码管理,后面会继续介绍其他功能。
