在分布式系统中,延迟任务(或限时任务)是一种常见的需求,通常用于实现延迟执行、定时处理或消息超时等场景。Redis 作为高性能的内存数据库,具备非常灵活的 Sorted Set(有序集合) 数据结构,可以很容易地实现延迟队列,满足限时任务的需求。
在本篇文章中,我们将介绍如何通过 Redis 和 Spring Boot 3 来实现 限时任务(也称为延迟任务或延迟队列),让你能够轻松管理任务的延时执行。
1. 延迟任务的场景
延迟任务的应用场景非常广泛,包括但不限于以下场景:
- 订单超时取消:用户下单后未支付,超过一定时间自动取消订单。
- 消息超时重发:当消息发送失败,可以延迟重试。
- 定时提醒:比如发送通知或定时邮件。
这些场景都需要任务在一段时间后自动执行,因此我们需要一种灵活、高效的解决方案来处理这类限时任务。
2. Redis Sorted Set基本原理
Redis Sorted Set(有序集合)是一种数据结构,它将元素存储在一个有序的集合中,每个元素都有一个唯一的分数(score)与之关联。Sorted Set 的基本原理如下:
- 元素和分数:每个元素都有一个唯一的分数与之关联,分数可以是整数或浮点数。
- 有序集合:元素按照分数的大小顺序存储在集合中,分数越小的元素越靠近集合的头部。
- 唯一性:集合中每个元素的分数必须是唯一的,如果两个元素的分数相同,则后一个元素会覆盖前一个元素。
- 插入和删除:元素可以通过
ZADD命令插入到集合中,通过ZREM命令删除元素。 - 范围查询:可以通过
ZRANGE命令查询集合中某个范围内的元素,范围可以是分数范围或索引范围,ZRANGEBYSCORE可以根据 score 范围查找元素。 - 分数更新:可以通过
ZINCRBY命令更新元素的分数。
Sorted Set 的底层实现使用了跳跃表(Skip List)数据结构,跳跃表是一种高效的有序数据结构,它可以在 O(log n) 的时间复杂度内进行插入、删除和查找操作。
3. 使用 Redis Sorted Set 实现延迟队列
在实现延迟任务时,我们可以将任务的执行时间作为 Sorted Set 中的 score,然后按时间顺序处理任务,确保在指定时间执行。
3.1. 引入依赖
首先,在 pom.xml 中引入 Redis 相关依赖,相关配置请参考重学SpringBoot3-集成Redis(一)基本使用:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
3.2. 配置 Redis
在 application.yml 中配置 Redis 的连接信息:
spring:
data:
redis:
host: 1.94.26.81
port: 6379 # Redis 端口
password: redis123456 # 如果有密码可以在这里配置
lettuce:
pool:
max-active: 100 # 最大并发连接数
max-idle: 50 # 最大空闲连接数
min-idle: 10 # 最小空闲连接数
3.3. 延迟队列的任务存储和处理
接下来,我们通过 Redis 的 Sorted Set 来存储任务,并定时检查任务是否到期。
3.3.1 任务存储
每当有新的任务需要延迟执行时,我们将其加入到 Redis 的 Sorted Set 中,score 为该任务的执行时间戳。
package com.coderjia.boot310redis.service;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @author CoderJia
* @create 2024/10/7 下午 05:10
* @Description
**/
@Service
public class DelayedTaskService {
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;
private static final String DELAYED_QUEUE_KEY = "delayedQueue";
// 添加任务到延迟队列
public void addTaskToQueue(String taskId, long delayInSeconds) {
long executeTime = System.currentTimeMillis() + TimeUnit.SECONDS.toMillis(delayInSeconds);
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().add(DELAYED_QUEUE_KEY, taskId, executeTime);
System.out.println("Added task " + taskId + " to the queue, will be executed in " + delayInSeconds + " seconds.");
}
}
3.3.2 任务处理
为了定期检查是否有任务到期,我们使用 Spring 的 @Scheduled 注解创建一个定时任务,定时从 Redis 中获取即将到期的任务并执行。
package com.coderjia.boot310redis.config;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* @author CoderJia
* @create 2024/10/7 下午 05:10
* @Description
**/
@Slf4j
@Service
public class DelayedTaskProcessor {
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;
private static final String DELAYED_QUEUE_KEY = "delayedQueue";
// 定时任务,检查是否有任务到期
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 5000) // 每隔5秒执行一次
public void processDelayedTasks() {
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Set<String> tasks = redisTemplate.opsForZSet().rangeByScore(DELAYED_QUEUE_KEY, 0, currentTime);
if (tasks != null && !tasks.isEmpty()) {
for (String taskId : tasks) {
// 执行任务
executeTask(taskId);
// 从队列中移除已执行的任务
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().remove(DELAYED_QUEUE_KEY, taskId);
log.info("Task " + taskId + " is executed.");
}
}
}
// 模拟任务执行
private void executeTask(String taskId) {
// 执行任务
log.info("Task " + taskId + " is executing...");
}
}
在这个示例中:
addTaskToQueue(String taskId, long delayInSeconds)方法将任务加入到 Redis 的 Sorted Set 中,延迟delayInSeconds秒执行。@Scheduled(fixedRate = 5000)每隔 1 秒扫描一次 Redis,查找是否有任务的执行时间已到期。如果有,则执行该任务,并从队列中移除。
3.4. 测试效果
在你的业务逻辑中调用上面创建的 addTaskToQueue 方法添加任务到延迟队列中去。
package com.coderjia.boot310redis.demos.web;
import com.coderjia.boot310redis.service.DelayedTaskService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author CoderJia
* @create 2024/10/7 下午 05:18
* @Description
**/
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class DelayedTaskController {
@Autowired
private DelayedTaskService delayedTaskService;
@GetMapping("/addDelayedTask")
public String addDelayedTask(@RequestParam("taskId") String taskId, @RequestParam("delay") Long delay) {
log.info("Adding task to the queue, taskId:{}, delay:{}", taskId, delay);
delayedTaskService.addTaskToQueue(taskId, delay);
return "Added task success";
}
}
3.4.1 测试添加任务
执行以下请求添加 3 条任务到延迟队列中,
http://localhost:8080/addDelayedTask?taskId=3&delay=20
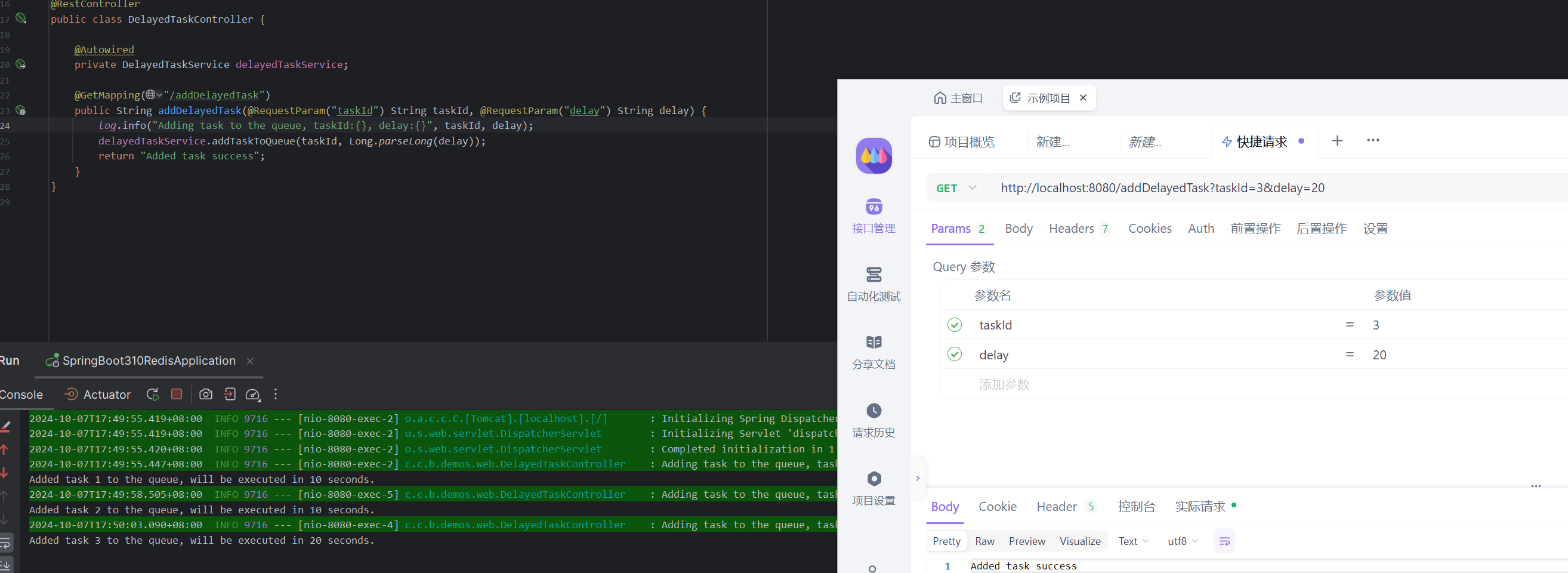
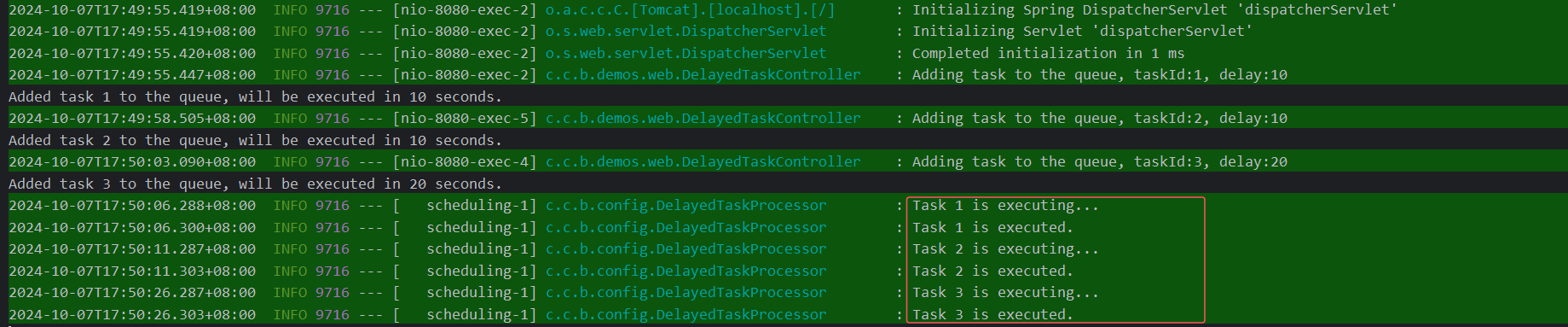
新增2条任务,先添加任务的后执行,测试效果。
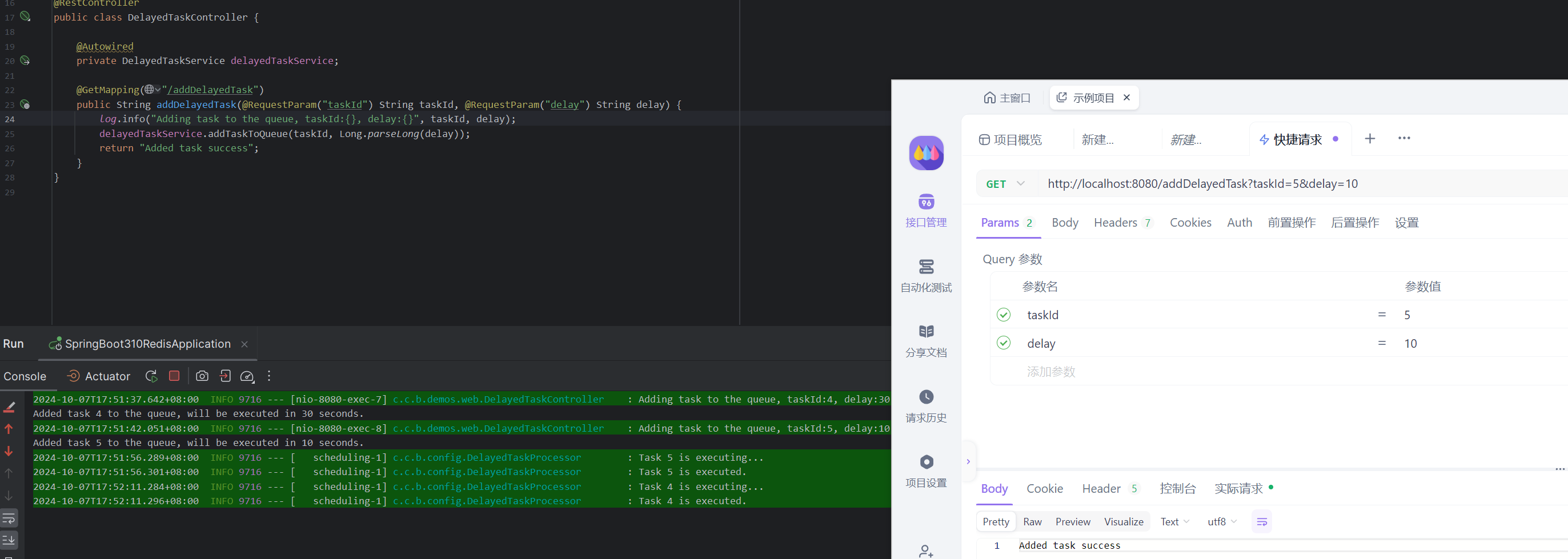
3.4.2 存储格式
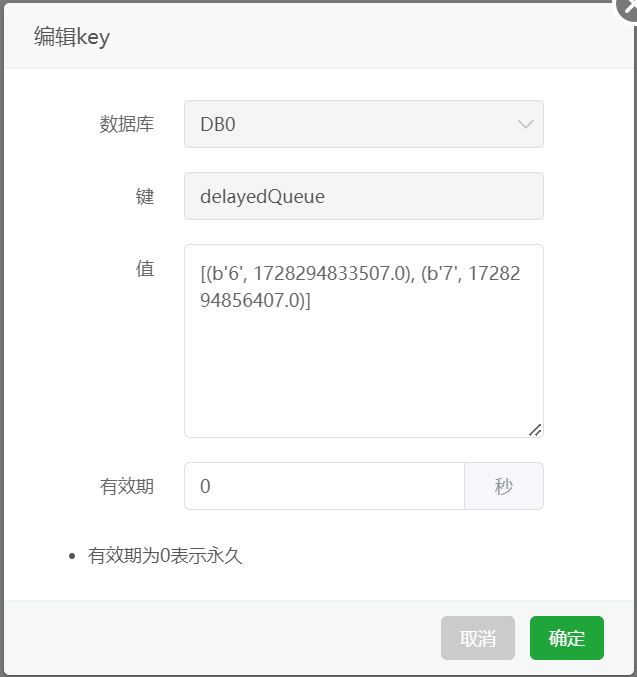
4. 优化建议
4.1. 任务幂等性
在分布式环境中,任务可能会被多个节点同时执行。确保任务的幂等性非常重要,可以通过 Redisson 分布式锁来保证同一时刻只有一个节点在执行任务。
// 获取分布式锁
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock("scheduledTaskLock");
try {
// 尝试获取锁,最多等待 1 秒,锁定时间 10 秒
if (lock.tryLock(1, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
try {
// 执行任务
System.out.println("Executing distributed scheduled task...");
} finally {
lock.unlock(); // 释放锁
}
} else {
System.out.println("Another instance is executing the task...");
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
4.2. 持久化
延迟队列可以与持久化存储结合起来,确保任务在 Redis 失败或重启时不会丢失。可以使用 Redis 持久化功能或将任务信息存储在数据库中。
4.3. 高并发处理
对于大量延迟任务,可以通过增加 Redis 集群的规模或使用更高效的数据结构来提升处理性能。
5. 总结
通过 Redis Sorted Set 和 Spring Boot 3,我们可以轻松实现限时任务的调度。Redis 的高性能和有序集合特性为我们提供了实现延迟队列的基础,而 Spring Boot 的定时任务调度则帮助我们定期处理这些任务。
在实际场景中,限时任务的应用非常广泛,比如订单超时处理、消息重发等场景,借助 Redis 我们可以有效管理这些延迟任务并确保系统的高效运行。
希望这篇文章能够帮助你更好地理解如何使用 Spring Boot 3 与 Redis 实现延迟队列。如果你在项目中遇到了相关问题,欢迎在评论区分享你的问题与经验。
